BitViraj Technologies - Your Gateway to
Tomorrow's Innovations

By Bitviraj Technology
Decentralized Identity & Verifiable Credentials Model
Decentralized Identity & Verifiable Credentials: A Trust-Based Digital Identity Model
Introduction: Why Digital Identity Is Fundamentally Broken
Every major digital service today-banking, insurance, healthcare, government portals-depends on identity. Yet the way identity works online is deeply flawed. We copy documents. We upload selfies. We trust centralized databases we don't control. Breaches expose millions of users at once. Verification is slow, repetitive, and expensive.
The problem isn't lack of technology. The problem is who controls identity and who is forced to trust whom.
Decentralized Identity (DID) and Verifiable Credentials (VCs) introduce a new mental model:
Identity is not stored in a central database. It is held by the individual and proven only when required.
This blog explains that model-clearly, practically, and without hype.
The Core Shift: From "Who You Are" to "What Can Be Proven"
Traditional identity systems ask:
Who are you?
Where do you live?
What is your full name and document number?
Decentralized identity asks a better question:
What claim needs to be proven right now?
"Is this driver licensed?"
"Is this person over 18?"
"Is this workshop IRDAI-registered?"
You don't need to reveal your entire identity to answer these questions. You only need a verifiable claim, cryptographically proven.
That is the philosophical foundation of DIDs and VCs.
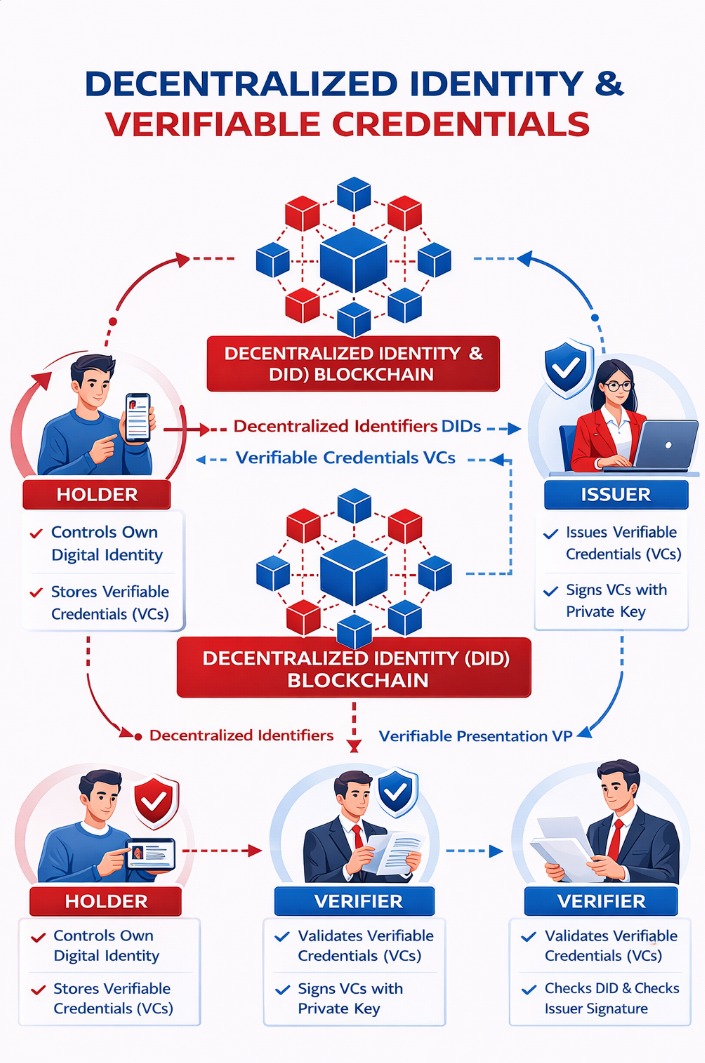
Key Building Blocks of the Trust Model
Let's break the system into simple, real-world roles.
Holder - The Identity Owner
The Holder is usually a person or organization.
What makes this model different is control:
The holder owns their digital identity
Credentials are stored in a secure wallet (mobile or enterprise)
Nothing is shared without explicit consent
No central authority can revoke access to your identity wallet.
Issuer - The Source of Truth
An Issuer is an authority trusted to make a specific claim.
Government
→ issues identity or license credentials
University
→ issues degree credentials
Insurer
→ issues policy credentials
Employer
→ issues employment credentials
The issuer:
Creates a Verifiable Credential
Digitally signs it with a private key
Publishes its DID (public identity) on a blockchain
Importantly, issuers do not store user data after issuance.
Verifier - The Party That Needs Proof
A Verifier doesn't want your documents. It wants cryptographic certainty.
The verifier:
Requests a specific claim
Receives a Verifiable Presentation (VP)
Checks the issuer's signature
Confirms credential integrity using the blockchain
No phone calls. No manual checks. No PDFs.
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs): Identity Without a Central Registry
A DID is a globally unique identifier that:
Is created by the user or institution
Is anchored on a decentralized network (blockchain)
Resolves to public keys and service endpoints
Think of it as: A digital passport number that no one else owns or controls.
Unlike usernames or Aadhaar numbers:
No central database owns the DID
No single authority can shut it down
Trust is established through:
Cryptography, not reputation
Mathematical proof, not institutional authority
Verifiable Credentials (VCs): Tamper-Proof Digital Claims
A Verifiable Credential is a cryptographically signed statement.
Example: "This person holds a valid motor insurance policy until Dec 2026."
What makes VCs powerful:
Cryptographically signed by issuer
Tamper-evident
Selectively disclosed (share only what's needed)
Verifiable offline or online
VCs can be revoked, updated, or time-bound-without reissuing identity.
The Role of Blockchain: Trust Without Surveillance
Blockchain is often misunderstood here.
Blockchain does not store personal data.
Instead, it stores:
Issuer DIDs
Public keys
Credential schemas
Revocation registries
This ensures:
No central verification authority
Public auditability
Cryptographic trust at internet scale
The blockchain acts as a trust anchor, not a data warehouse.
End-to-End Credential Flow
Issuer creates a credential
→ Signs it with its private key
Holder stores the credential
→ In a personal or enterprise wallet
Verifier requests proof
→ "Show valid license"
Holder shares a Verifiable Presentation
→ Only relevant fields
Verifier validates cryptographically
→ Using issuer DID on blockchain
No phone calls. No PDFs. No trust assumptions.
Why This Model Is a Game-Changer
Privacy by Design
Users share minimum required information, not entire documents.
Fraud Reduction
Forged documents fail cryptographic checks instantly.
Cost Efficiency
Manual verification teams become unnecessary.
Regulatory Alignment
Supports consent, auditability, and data minimization principles.
Interoperability
Credentials work across platforms and borders.
Real-World Use Cases That Actually Matter
Insurance
Fraud-proof policy issuance
Instant claim verification
Portable no-claim history
Banking & Fintech
Reusable KYC credentials
Faster onboarding
Reduced compliance cost
Supply Chain
Verified manufacturer identities
Compliance credentials for vendors
Audit-ready documentation
Government & DPI
Citizen-controlled digital identity
Cross-department trust
Reduced data duplication
What Decentralized Identity Is Not
Let's clear misconceptions:
Not cryptocurrency identity
Not public storage of personal data
Not anonymous by default
Not replacing government authority
It redefines how authority, proof, and trust interact digitally.
The Bigger Picture: Trust as Infrastructure
In the internet's early days, we built:
Networks to move data
Platforms to host services
APIs to integrate systems
What we did not build was trust infrastructure.
Decentralized Identity and Verifiable Credentials are exactly that: Trust as a shared, neutral, programmable layer.
Once trust becomes infrastructure, innovation accelerates-safely.
Final Thought: Identity Should Work for People, Not Platforms
The future of digital identity is not about better databases.
It's about changing the power structure of trust.
Decentralized Identity ensures:
People own their identity
Institutions issue truth
Verification happens without blind trust
That is not just a technical upgrade.
It is a structural correction to the internet itself.
Case Studies
Empowering Digital
Evolution
Blogs
Empowering Digital
Evolution
BitViraj Technologies - Your Gateway to
Tomorrow's Innovations
Embark on a DigitalJourney


The next-generation digital technology company Bitviraj has the potential to empower and reinvent business in the current fast-paced market.
Our Service
- Website Development
- Application Development
- Blockchain Development
- Gaming and Metaverse








